Mangrove Wall Protecting Odisha From Cyclones: The mangrove forests, or hental bana, of Bhitarakanika are known as natural barriers that protect the land from the strong winds of cyclones. These natural cyclone shelters are designed to safeguard coastal areas from the impacts of severe weather events.
Mangrove Wall Protecting Odisha From Cyclones
Mangroves play a vital role in protecting coastal regions from cyclones and other extreme weather. They act like a protective wall, helping to reduce wind speed and lessen the impact of cyclones in the coastal zone.
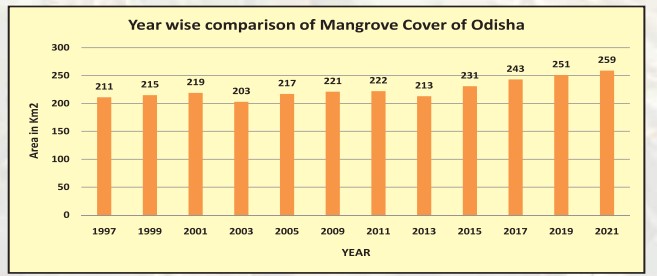
According to state records, Kendrapada has the highest mangrove cover in Odisha, with nearly 209.25 sq. km of mangrove forests, followed by Bhadrak. Bhitarakanika is the 2nd largest mangrove ecosystem in India.
How They Reduce the Impact of Cyclones
Mangrove plants are distinct from terrestrial plants; they are specialized trees and shrubs that thrive in coastal intertidal zones, where saltwater and freshwater mix. They grow naturally, creating a wall-like structure. When strong winds from a cyclone approach land, they first collide with the mangrove plants. This interaction reduces the strength of the wind and the intensity of waves, thereby decreasing their impact on coastal areas and helping to prevent soil erosion. 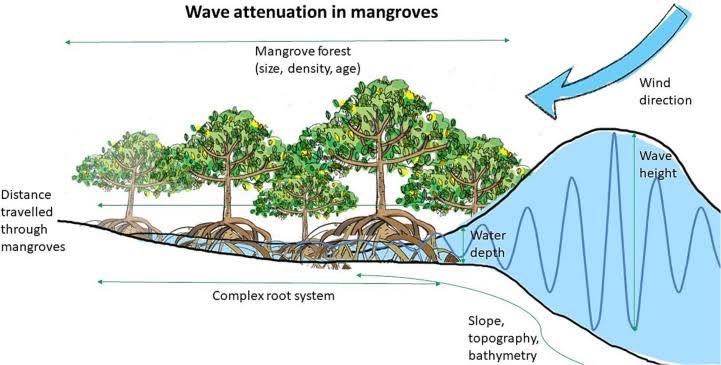
A Scale model showing how Mangrove Forests protect coasts From wave erosion
In the coastal belt of Odisha, especially in Kendrapada and Bhadrak, the mangrove forests are essential. The more we protect these mangrove plants, the better we can safeguard ourselves from the impacts of cyclones.
Odisha has added 537.44 Sq Km forest cover & topped among all states in increasing mangrove cover in last 2 yrs. Odisha ranked 3rd in growth of forest cover among states as per India State of Forest Report 2021, compared to 2019 assessment.




